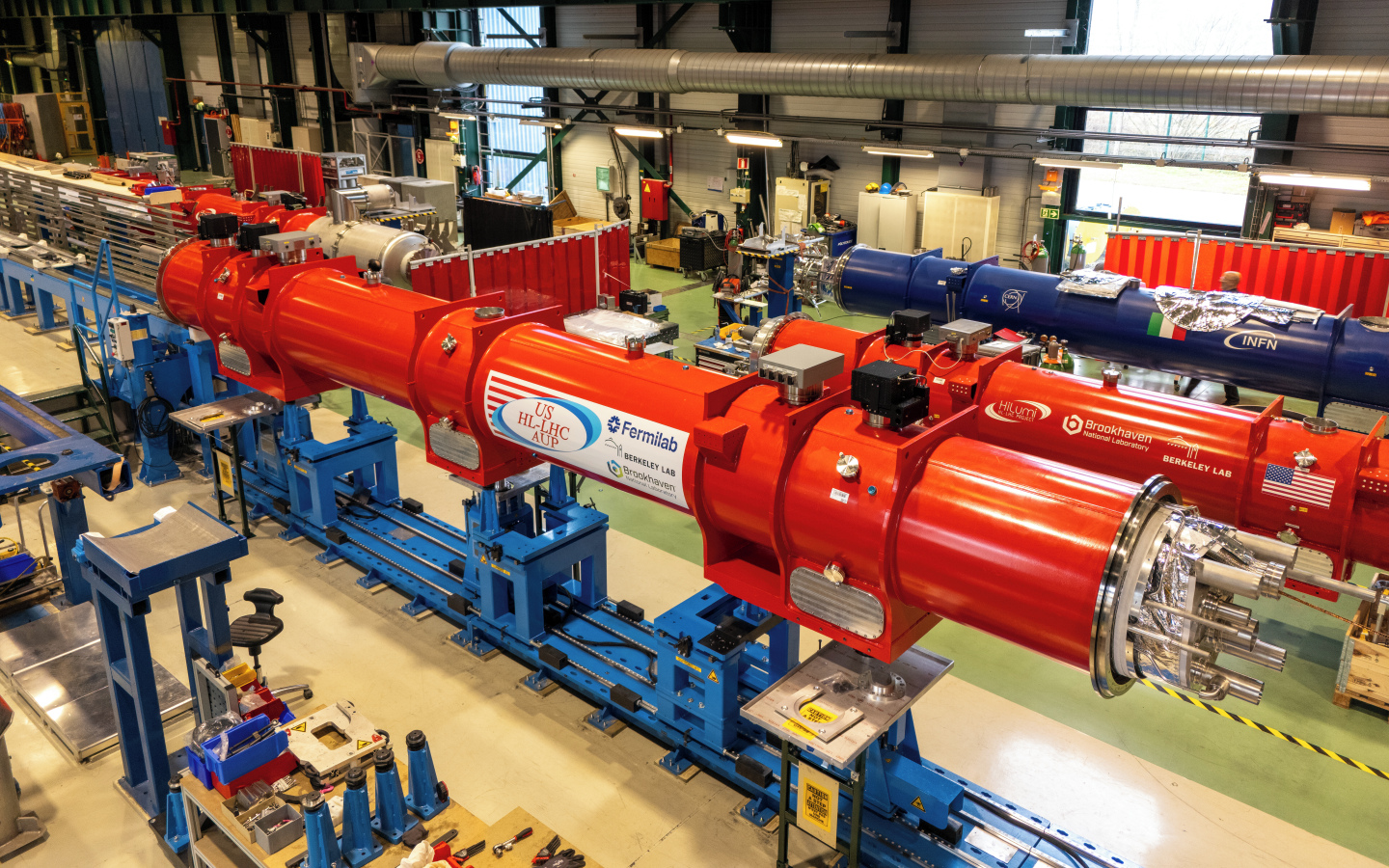

Magnet Welding Support
Assembling service modules for the new HL-LHC inner triplet magnets cryostats
Overview
As part of the HL-LHC upgrade, new cryo-assemblies are being produced at the SMI2 workshop for the inner triplet magnets of IR1 and IR5. Each assembly consists of a Phase 1 cryostat—the vacuum vessel, thermal shields, and cold-mass supports—and a Phase 2 service module, which provides the external interfaces needed for installation in the LHC tunnel.
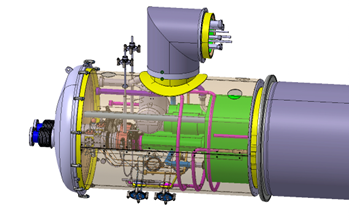
Our work concerns Phase 2, focusing exclusively on the service module. This module integrates the cryogenic, vacuum, electrical, and mechanical connection systems required to link the cryostat to the HL-LHC infrastructure. It includes the piping, expansion joints, alignment interfaces, and technical services that enable proper operation once installed in the tunnel.
This activity forms part of WP3, which oversees the design and assembly of the HL-LHC magnet systems. The MME-FW section plays a key role in ensuring the mechanical integrity, weld quality, and long-term reliability of the service-module components.
Challenge
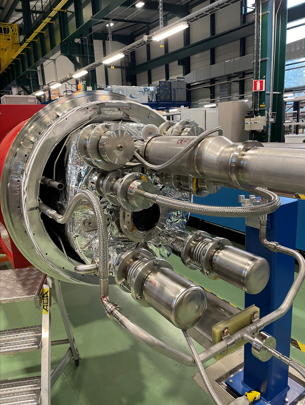
The service modules must meet stringent requirements for liquid-helium tightness, compliance with pressure-equipment regulations (PED), and reliable integration with both the cryostat and the tunnel infrastructure. The welding operations involved in assembling the service-module piping, bellows, and interfaces are particularly critical, as they must comply with ISO 3834-2 standards and remain reliable under cryogenic operating conditions.
Coordinating these fabrication activities—while maintaining full traceability, documentation, and quality control—is challenging, especially given the tight project schedule and the advanced technologies involved in the HL-LHC magnet systems. These constraints require close collaboration between engineering, quality assurance, and production teams to ensure consistent and safe integration of the service modules into the overall cryo-assembly.
Solutions
The fabrication of the service modules at SMI2 relies on advanced welding technologies and materials selected to withstand the demanding HL-LHC operating conditions. Automated and orbital welding processes are widely employed on stainless-steel piping, manifolds, and bellows, ensuring consistent quality and high repeatability for components that must remain leak-tight at cryogenic temperatures. Aluminum parts, used for thermal and structural functions, are assembled using welding techniques adapted to cryogenic applications.
Manual welders, qualified according to relevant ISO standards, work in close coordination with welding engineers who oversee every stage of production—from WPS development and procedure validation to in-process control and NDT follow-up. This integrated workflow ensures high weld quality, full traceability, and reliable integration of the service modules into the overall cryogenic system.
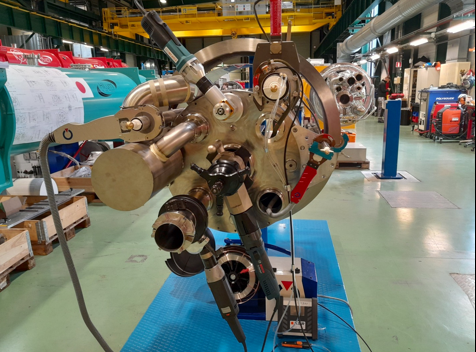
Outcome of HL-LHC Service-Module Fabrication at SMI2
The fabrication of the HL-LHC service modules at SMI2 is progressing successfully, supported by automated, orbital, and specialized manual welding techniques adapted to cryogenic and PED-compliant applications. Qualified welders and welding engineers collaborate throughout WPS development, procedure qualification, in-process monitoring, and NDT, ensuring high weld quality and full traceability.
This coordinated approach enables the service modules to meet the stringent requirements for helium tightness, pressure-equipment compliance, and long-term operational reliability within the HL-LHC cryogenic system. The progress achieved highlights CERN’s strong capabilities in precision cryogenic fabrication and reinforces the project’s readiness for the upcoming installation phases.
FIND OUT MORE
Keen to learn more about our activities?
Find out what the Forming and Welding Section can do for you.

